PREVENTING A RANSOMWARE DISASTER
Ransomware is not just another cyberattack; it can quickly proliferate through shared folders.
Contents
INTRODUCTION
THE RISE OF RANSOMWARE
WHAT IS RANSOMWARE AND HOW DOES IT SPREAD?
REALITY OF RANSOMWARE
WHAT CAN BE DONE?
BACKING UP YOUR DATA WITH SPANNING
CONCLUSION
Ransomware is a threat to businesses that costs millions of dollars each year and continues to grow in sophistication. Fortunately, Spanning Backup protects your SaaS applications from data loss with easy-to-deploy, efficient backup and restore solutions for Google Workspace, Microsoft 365 and Salesforce.
INTRODUCTION
Ransomware is a significant menace and continues to threaten businesses of all shapes and sizes. Researchers from Zscaler ThreatLabz found that ransomware attacks increased by 80% year-over-year. According to a recent poll conducted by ThoughtLab, security executives across the globe expect attacks will continue to increase over the next two years. Misconfigurations, human error and poor IT hygiene are considered to be the leading causes for the rising success rates of these attacks.
Using a variety of attacks, including targeted emails and infected websites, criminals can inject malware into your network, which then holds your data or other systems hostage until you pay a ransom. It's very difficult to block every ransomware attack, so many experts, including the FBI, advise organizations to have a layered defense with protected backups to enable a fast recovery.
Organizations following this advice often focus on key internal systems and forget about their endpoints — desktops and laptops — and SaaS applications, like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, which contain data that is critical for employees to function. Fortunately, Spanning Backup protects your SaaS applications from data loss with easy-to-deploy, efficient backup and restore solutions for Google Workspace, Microsoft 365 and Salesforce.
Never before in the history of humankind have people across the world been subjected to extortion on a massive scale as they are today.
THE RISE OF RANSOMWARE
Ransomware in not a new phenomenon. In fact, it has been around since the 80s. In 1989, the first-known malware — the “AIDS Trojan", was distributed through infected floppy disks to attendees of the World Health Organization's AIDS conference. The Trojan, also known as "PC Cyborg," hid the files in the victim's computer hard drive and encrypted the file names. The malware then displayed a message to the victims, demanding they pay $189 to regain access.
Since then, ransomware has become more prominent, dangerous and sophisticated. Ransomware dominated the cybercrime landscape in 2021 and there's no sign of it slowing down in 2022. Although some of the most notorious ransomware variants like DarkSide, Ryuk and REvil (also known as Sodinokibi) seem to have disappeared, newer variants like Hive Ransomware, AvosLocker and HelloKitty (first seen in 2020) are emerging and are expected to become more prevalent just like their predecessors.
According to Sophos The State of Ransomware 2021 report, while the number of ransomware attacks are declining, the severity and cost of remediation of ransomware attacks are increasing significantly. The report found that the average cost to rectify a ransomware attack more than doubled to $1.85 million in 2021.
That said, with Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and open-source versions of ransomware easily available today, ransomware attacks are poised to grow in number and complexity in 2022 and beyond. Here's an interesting, RaaS project hosted on GitHub that demonstrates how easy ransomware is to make.
Although ransomware knows no geographical boundaries, the top six countries affected by this type of malware in 2021 were India (68%), Austria (57%), the United States (51%), Israel (49%), Turkey (48%) and Sweden (47%).
Emotet Malware Is Back!
Emotet malware resurfaces after disappearing for almost a year. Emotet was one of the most dangerous botnets before being taken down by law enforcement agencies in 2021. This was a big relief since it was widely used by cybercriminals to distribute malware through spam emails. Emotet was capable of performing several functions like stealing sensitive information, spamming and distributing malware. Due to its mischievous nature, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) considers Emotet to be among the most costly and destructive malware affecting state, local, tribal and territorial (SLTT) governments as well as the private and public sectors.
Just when law enforcement and security researchers thought Emotet was history, the notorious malware reappeared in mid-November 2021. According to Threatlabz research team's technical analysis, there has been some changes in the command and control data as well as the encryption used. Another change is the use of HTTPS instead of plain HTTP for command and control communication. The reincarnated Emotet is believed to be utilized for what it was popularly known for — providing initial access to hackers. Emotet was one of the most powerful and destructive malicious programs that impacted governments as well organizations worldwide. As such, its reappearance is a major cause for concern.
WHAT IS RANSOMWARE AND HOW DOES IT SPREAD?
Ransomware is not just another cyberattack; it can quickly proliferate through shared folders, affecting both those within and outside the infected organization. Ransomware either locks the computer (locker ransomware) or encrypts the user's files (crypto ransomware) and then demands that the user pay a specified amount of money — usually a digital payment such as Bitcoin — in exchange for a decryption key that unlocks the computer or files.
Ransomware gains access to a computer system by way of a network's weakest link, which is typically a user's email or social networking site. Once a user clicks on a malicious link or opens an infected attachment, the malware spreads throughout the system.
Once opened, fake PDF files, fabricated FedEx and UPS notices, and fraudulent financial institution correspondence that are infected with malware can quickly bypass an organization's network security and spread beyond the local system through network drives and other endpoints tied to file sync and share tools such as Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive and Dropbox.
According to the United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT), cybercriminals who use ransomware are so effective because they instill fear and panic into their victims, in part by displaying intimidating messages such as: “Your computer was used to visit websites with illegal content. To unlock your computer, you must pay a $100 fine.” Ransomware-as-a-Service allows anyone, even those with little or no programming experience, to pay for and use already-developed malware to launch sophisticated cyberattacks. With a plethora of RaaS options available today, all that is required from a wannabe cybercriminal is malicious intent and access to the dark web.
The gist of ransomware is simple: if you don't pay the ransom, you forfeit access to your computer and the data that's on it. And you further forfeit access for others to shared documents and data, compounding the impact exponentially. Unfortunately, victims who pay the ransom might still not get their files back.
The harsh reality is that the attacker might not supply the decryption keys. In fact, a recent survey found that of those victims of ransomware who paid the ransom, 96% got their data back. However, only 65% of the encrypted data was restored even after paying the ransom.
REALITY OF RANSOMWARE
The rise of ransomware has moved more from targeting consumers to organizations. According to the APWG's Phishing Activity Trends Report, phishing attacks reached an all-time high in the first quarter of 2022, with a total of 1,025,968 attacks.
Data that's key to an organization's daily operations or subject to regulatory compliance must always be protected. Hackers don't necessarily care who the information belongs to; they will do their best to exploit any weakness in the IT infrastructure to steal, damage or hold for ransom an organization's data.
Businesses know that it's very difficult to protect against every threat, but ransomware is particularly challenging. Companies have to maintain focus on business continuity, which can lead them to be more likely to entertain paying a ransom.
Crypto ransomware, such as CryptoWall or Locky, account for the majority of all ransomware. According to Sophos The State of Ransomware 2022, more than 70% of organizations surveyed experienced an increase in cyberattacks. The respondents also noted that they witnessed increased complexity and impact of cyberattacks. Additionally, more than 65% of organizations suffered a ransomware attack in 2021. The report also revealed that threat actors have become more successful at encrypting data, as was the case in 65% of attacks.
“Never before in the history of humankind have people across the world been subjected to extortion on a massive scale as they are today.”
Effectively defending against ransomware requires not only threat detection and prevention, but a backup and recovery strategy. Failing to do so can result in significant costs. According to Palo Alto Networks' Unit 42 consultants, the average ransomware payment in 2022 increased by a staggering 71% to $925,162 compared to 2021.
Finally, consider Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). This is becoming the newest concept in the blackhat community as developers create tools that can be sold en masse to smaller criminals to then be launched against individuals and companies. This gives everyone involved a “piece of the action” and allows the dispersal mechanism to be co-opted out and decentralized.
WHAT CAN BE DONE?
So how do companies mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks in their organizations? A consistent and defense-in-depth, multilayer approach that involves software vendors, customers, ops, processes and security is critical.
It is important to note that common backup solutions, such as a USB drive or network-attached storage device (NAS), are not reliable methods for backing up and safeguarding your data.
Ransomware typically spreads throughout an organization's entire file system, including an attached drive or network share, encrypting both production data and backup data.
The most reliable form of protection organizations can leverage to safeguard their data is backup. The more your backup supports fast, easy restore to the pre-infection state, the less likely you will suffer a massive failure of business continuity.
Like most criminals, cyber criminals are opportunists who seek out easy targets. Are you an easy target? For starters, consider these questions:
- How are you backing up your data?
- How are you educating you employees about cyber-risks (e.g., unsolicited emails)?
- What cadence is established to ensure firewalls and mail filters are up to date?
- How do you ensure your antivirus software is up to date?
- How do you sync data from endpoints to cloud-based file sync share systems?
Having a viable backup and recovery plan is not just a sound operational practice. It is often required by law or regulation, depending on your organization's industry or type:
- HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to have and periodically test a viable data backup and disaster recovery plan for their electronic protected health information.
- Two financing and banking enforcement arms, the OCIE and FFIEC, have made cybersecurity — including the ability to recover from incidents — a key part of their enforcement and audit priorities.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has reminded public companies of their need for adequate cyber controls, which include backup and recovery functions, and responsibility to disclose material cybersecurity risks. In today's world, certainly the inability to recover from an increasingly common threat such as ransomware could rise to the level of disclosure.
In the event of hardware failure, theft, virus attack (including a ransomware extortion plot), accidental deletion, or natural or manmade disaster, if you have the right backup and recovery solutions in place, you can ensure that your data will be available and can be restored to its original state, and that your organization is compliant with applicable regulations.
When looking for a backup solution, what should you evaluate to ensure that your data is protected?
Consider the following:
- What data (including SaaS data) could be targeted?
- How do you get a copy of backups offsite?
- How do you verify backups are happening successfully?
- How do you verify that data can be restored to its original state?
- How do you ensure your encrypted data can be quickly restored?
- How do you restore your backup to a specific point-in-time?
BACKING UP YOUR DATA WITH SPANNING
Implementing a backup system is a critical step in your data protection planning since it ensures you are well prepared to quickly recover from data loss — not just from ransomware attacks but also from other malicious attacks, end user errors, and configuration or sync errors.
Having a granular, complete and trusted backup service in place protects you in two ways:
- First, your data is safe and can be restored from any point in time, easily by your IT admin.
- Second, you won’t have to consider paying ransom to hackers since you still have access to an unencrypted version of your data.
IT STARTS AT THE ENDPOINT
Recovering servers doesn't guarantee you've removed the infection from your network because it probably started at the endpoint as illustrated below.
Data that's backed up by Spanning is isolated from the customer network and cannot be infected or propagate an infection.
SaaS productivity platforms such as Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 are also vulnerable to malware attacks, and Google or Microsoft may not be able to roll back your files to a pre-infected state.
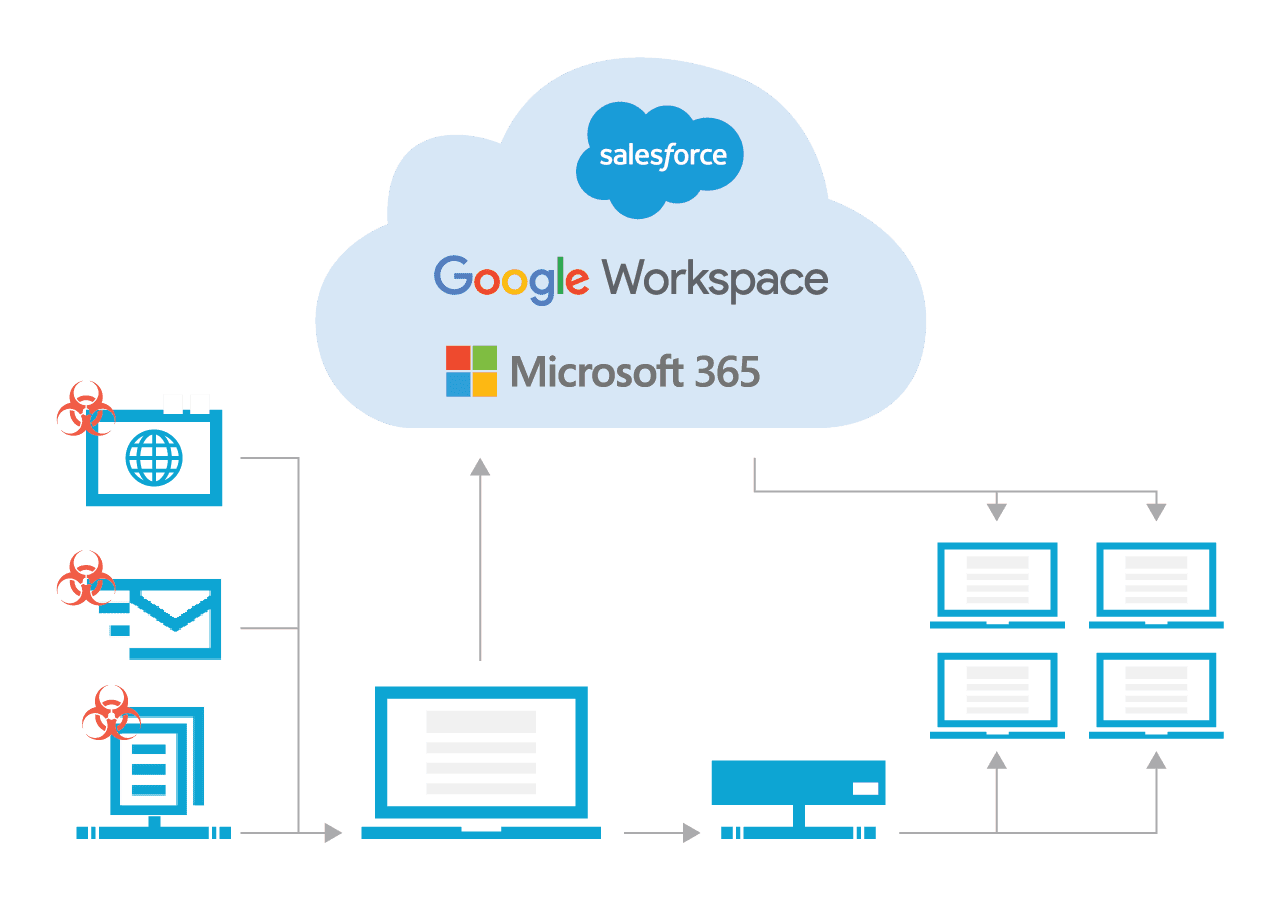
ENDPOINT AND CLOUD ISOLATED RECOVERY
- Removing laptop infection requires reformatting and results in lost data.
- Removing cloud infection requires deleting all infected files from the cloud.
- Spanning ensures laptops and cloud do not re-infect network once cleaned.
- Spanning is isolated from customer network and cannot be infected or propagate infection.
Infected endpoint devices can sync with these platforms, and in some cases the malware can automatically proliferate through shared drives and folders, encrypting files shared within your and even outside of your organization.
Spanning Backup fully protects data that is stored and generated in Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 and enables you to rapidly recover data from a previous point in time, before the files were encrypted by ransomware.
That means your data is safe, secure and always available. These solutions ensure that you can respond to and recover from an attack, and rapidly restore your data to its original state for business continuity and to meet recovery time and recovery point objectives.
– Palo Alto Networks
CONCLUSION
According to Zscaler ThreatLabz, APWG and Sophos, ransomware is utilizing many new avenues for infection: email, brute force, self-propagation, OS vulnerabilities and third-party app stores. Although prevention and detection are critical, a regularly updated backup that enables rapid, accurate restores is the last line of defense.
"In today's data landscape, backup, disaster recovery and ransomware protection have become key components of organizational resiliency. With one ransomware attack taking place every 11 seconds, it is now more important than ever for organizations to understand the threats this poses to their business and their reputation. It is no longer a matter of if, but rather when a malicious attack or unplanned disaster will occur. However, the bright side is, there is a way to avoid paying ransom or suffering extended business downtime. How? By having a holistic, unified backup and disaster recovery strategy with immutable storage support, air-gapped copies of data, granular recovery and a well-rehearsed set of DR plans that are easily executable when disaster strikes."
Organizations rely on digitized data more than ever. As such, all organizations — from the smallest business to the largest enterprise — must take the necessary steps to ensure that their data is securely backed up and quickly restorable to its original state.
Spanning Backup solutions provide peace of mind by quickly and easily restoring your data exactly the way it was at any point in time should a data loss event strike.
Backup is one thing. Restore is everything. We deliver the most fine-tuned and user-friendly restore process available for Microsoft 365, Salesforce and Google Workspace.
See how Spanning 360 helps prevent, anticipate and mitigate account compromise and data loss.
A PDF version of this whitepaper is also available. Click the button below to download it instead.