Backup
Cloud and Data SecurityForming a Backup Strategy: 4 Steps to Follow
A comprehensive backup strategy is an essential part of an organization’s cyber safety net and it’s important to have one outlined & put in place before a data loss event occurs. Follow these four steps to help you form a strategy that is right for your organization.
By
Matt McDermott
4 minute read
With rising malware attacks and the escalating cost of a data breach – pegged at an average of $3.92 million – cybersecurity has emerged as a top business priority. However, even with tightened security measures, breaches have increased by 67% over the past 5 years. As a result, the need to have a solid backup strategy in place has become more important than ever. To be truly protected, organizations must form a well-defined plan that can aid in the quick and seamless recovery of lost data and guarantee business continuity when all preventive measures fail. A comprehensive backup strategy is an essential part of an organization’s cyber safety net. It can be defined as an administrator’s plan to ensure critical organizational data is backed up and available for restore in the case of a data loss event. A backup strategy, along with a disaster recovery plan, constitute the all-encompassing business continuity plan which is the blueprint for an organization to withstand a cyberattack and recover with zero-to-minimal damage to the business, reputation, and data.
Here we’ll detail four steps to develop a dependable backup strategy.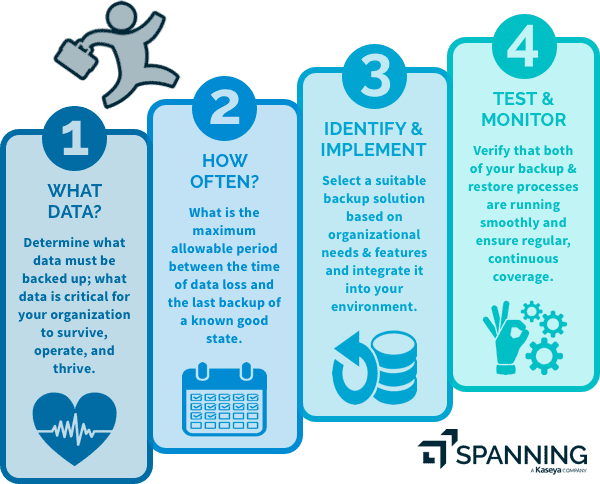 ## #1 Determine what data has to be backed up
## #1 Determine what data has to be backed up
“Everything” would probably be your answer. However, the level of data protection would vary based on how critical it is to restore that particular dataset. Your organization’s Recovery Time Objective (RTO), which is the maximum acceptable length of time required for an organization to recover lost data and get back up and running, would be a reliable benchmark when forming your backup strategy.
Assess and group your applications and data into the following:
- Existentially-critical for the business to survive
- Mission-critical for the organization to operate
- Optimal-for-performance for the organization to thrive
Once all pertinent data is identified, layer the level of protection accordingly.
#2 Determine how often data has to be backed up
The frequency with which you back up your data should be aligned with your organization’s Recovery Point Objective (RPO), which is defined as the maximum allowable period between the time of data loss and the last useful backup of a known good state. Thus, the more often your data is backed up, the more likely you are to comply with your stated RPO. As a good rule of thumb, backups should be performed at least once every 24 hours to meet acceptable standards of most organizations.
#3 Identify and implement a suitable backup and recovery solution
Based on your organization’s requirements, you need to identify a suitable backup solution as part of your backup strategy. Some aspects to consider:
- Types of backup: full backup, differential backups where only additions/changes are copied, and incremental backups where delta changes since the most recent incremental backup are copied.
- Where the data is backed up: Physical/Local backup where the data is backed up on-site using an external hard drive, USB drive or the like. Cloud/Remote backup, where data is backed up off-site in a cloud storage environment.
- Features your organization requires: Below are several essential aspects of a comprehensive and dependable backup and restore solution to consider:
- Ease of Backup: Automated and/or on-demand options
- Restore Flexibility: Cross-user, search-based, point-in-time
- Scalability: License and user management
- Ease of Use: Intuitive user interface and self-service recovery
- Post-purchase Experience: Free support and infinite backup
- Strong Credentials: Superior customer ratings, security & compliance certifications
#4 Test and Monitor your backup system
Once your backup system is in place, test it, both to check that the backup is successful and that the restore is smooth and accurate. Verify the backup and restore with regards to various types of artifacts – accounts, emails, documents, sites, etc. If the backup solution supports end-user backup – inform and educate your users about using it. Finally, remember to monitor your backup performance and regularly check the logs for data lapses.
Oftentimes, data and applications on the cloud are overlooked when planning a backup strategy, as SaaS data is assumed to be secure. While SaaS platforms and applications are exceptionally safe, they cannot protect you from data loss at your end or the 0.1% downtime. Spanning Backup provides cloud-to-cloud comprehensive data protection and fast, easy restore of Microsoft 365, Google Workspace and Salesforce. Take our customers’ word for it – we’re the highest rated backup and restore solution on the respective marketplaces.
Try Spanning Backup absolutely free for 14 days and see how we can be an integral part of your organization’s backup strategy.
Learn More About Spanning Backup