BackupTypes of Backup: Understanding Full, Differential, and Incremental Backup
There are 3 main types of backup: full, differential, and incremental. The right type of backup leads to the right SaaS backup strategy. Learn what each has to offer.
By
Dave Wallen
4 minute read
***A system failure wipes out all your data, corruption renders your data useless, an error leads to permanent deletion. Remember: Data loss always sneaks up on you.***The only way to tackle data loss incidents is by putting a solid backup strategy in place. In fairness, most companies today do back up their data rather diligently. Yet, one-third of them experience problems with backup restoration. The dichotomy lies in the way a ‘backup strategy’ is perceived.
For the majority, a backup strategy starts and ends with what to backup. For the rest, it’s about what and which type of backup to implement.
In light of World Backup Day, let’s move the discussion from ‘why backup’ to the types of backup. The former gives you a backup strategy while the latter gives you the right backup strategy.
How Many Types of Backup are There?
There are mainly three types of backup: full, differential, and incremental.
Let’s dive in to know more about the types of backup, the difference between them and which one would be the best fit for your business.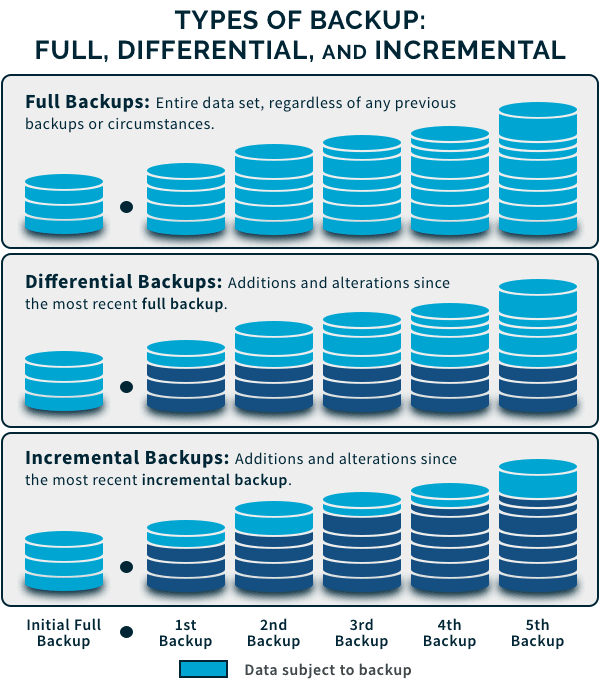 ### Full Backup
### Full Backup
A full backup is the most complete type of backup where you clone all the selected data. This includes files, folders, SaaS applications, hard drives and more. The highlight of a full backup is the minimal time it requires to restore data. However, since as everything is backed up in one go, it takes longer to backup compared to other types of backup.
The other common issue with running full backups is that it overloads storage space. That’s why most businesses tend to run a full backup and occasionally follow it up with differential or incremental backup. This reduces the burden on the storage space, increasing backup speed.
Differential Backup
A differential backup straddles the line between a full and an incremental backup. This type of backup involves backing up data that was created or changed since the last full backup. To put it simply, a full backup is done initially, and then subsequent backups are run to include all the changes made to the files and folders.
It lets you restore data faster than full backup since it requires only two backup components: an initial full backup and the latest differential backup.
Let’s see how a differential backup works:
Day 1 – Schedule a full backup
Day 2 – Schedule a differential backup. It will cover all the changes that took place between Day 1 and Day 2
Day 3 – Schedule a differential backup. It will make a copy of all the data that has changed from Day 2 (this includes the full backup on Day 1 + differential backup) and Day 3.
Incremental Backup
The first backup in an incremental backup is a full backup. The succeeding backups will only store changes that were made to the previous backup. Businesses have more flexibility in spinning these types of backups as often as they want, with only the most recent changes stored.
Incremental backup requires space to store only the changes (increments), which allows for lightning-fast backups.## Difference Between Full, Differential and Incremental Backups
| Full | Differential | Incremental |
|---|
| Storage Space | High | Medium to High | Low |
| Backup Speed | Slowest | Fast | Fastest |
| Restoration Speed | Fastest | Fast | Slowest |
| Media Required for Recovery | Most recent backup only | Most recent full backup & most recent differential backup | Most recent full backup & all incremental backups since full backup |
| Duplication | Stores a lot of duplicate files | Stores duplicate files | No duplicate files |
Difference Between Full, Differential and Incremental Backups
| Backup Type | Attributes |
|---|
| Full Backup | Storage Space: HighBackup Speed: SlowestRestoration Speed: FastestMedia Required for Recovery: Most recent backup onlyDuplication: Stores a lot of duplicate files |
| Differential Backup | Storage Space: Medium to HighBackup Speed: FastRestoration Speed: FastMedia Required for Recovery: Most recent full backup & most recent differential backupDuplication: Stores duplicate files |
| Incremental Backup | Storage Space: LowBackup Speed: FastestRestoration Speed: SlowestMedia Required for Recovery: Most recent full backup & all incremental backups since full backupDuplication: No duplicate files |
The Right Backup Strategy With the Right Type of Backup
Let’s celebrate World Backup Day by choosing the right type of backup, which often depends on the amount of data you need to backup.
For instance, if you have a high volume of data, you need a backup strategy that uses the combined power of a full and an incremental backup.
These insights offer clarity for your SaaS backup buying process and can help you narrow down your search for the right backup solution that meets your backup needs. After all, you want a reliable solution that will store your business information, like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365 and Salesforce data, and help you recover it when you need it.
Spanning, a Kaseya company, is the leader in SaaS Cloud-to-Cloud Backup, proven and trusted by more than 10,000 organizations to provide enterprise-class data protection for Microsoft 365, Google Workspace and Salesforce. It enables end users as well as administrators to easily backup and restore data in just a few clicks.
Learn More About Spanning Backup