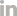What Is Multifactor Authentication (MFA)? How It Works, Examples & Benefits
Today, the cyberthreat landscape is expanding at an unprecedented pace. Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, relentless and damaging, posing significant risks to organizations of all sizes. From ransomware attacks to phishing scams, malicious actors are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise business-critical information. Unfortunately, various industry reports indicate that it’s only going to get worse in the coming years. According to Statista’s Cybersecurity Outlook, the global cost associated with cybercrime is expected to surge in the next few years, rising from $8.44 trillion in 2022 to $23.84 trillion by 2027.
Traditional security mechanisms are no longer sufficient to protect organizational data and infrastructure from this rapidly evolving threat landscape. Organizations must adopt proactive and robust security controls, and one such critical defense mechanism is multifactor authentication (MFA). Multifactor authentication is an authentication method or security control that adds an extra layer of security by necessitating users to provide multiple types of verification before gaining access to their accounts, systems or applications.
In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into the significance of multifactor authentication and explore why it’s a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Check out this blog to learn how Spanning Backup leverages an app-only authorization model (OAuth 2.0) and how it — along with Microsoft-authorized MFA — further enhances the protection of your cloud backups of Microsoft 365. Get a personalized demo now to discover how you can ensure comprehensive protection of your Microsoft 365 data with Spanning.
What is multifactor authentication (MFA)?
Multifactor authentication is an authentication method that requires more than just a password for accessing digital accounts, systems or applications. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by asking for two or more types of verification. This could include something the user knows, like a password, along with something the user has, like a smartphone or token, or even something they are, like a fingerprint or facial recognition.
Multifactor authentication is critical in today’s digital world, where cyberthreats are always looming. Relying solely on passwords can leave user accounts vulnerable to hacking. With multifactor authentication, even if a hacker manages to obtain a user’s password, they will still need additional authentication factors to gain access. This makes it significantly harder for them to infiltrate systems and steal data, highlighting the importance of multifactor authentication.
MFA vs 2FA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a form of multifactor authentication, but it differs from MFA in the number of verification methods required. As discussed above, MFA mandates two or more forms of verification, such as a password, code sent to a phone and fingerprint scan. On the other hand, 2FA requires only two methods, typically a password paired with a secondary verification, like a texted code. While both enhance security, MFA offers a higher level of protection.
Why is multifactor authentication important?
Multifactor authentication is crucial for organizations and IT professionals due to its proven effectiveness compared to relying solely on passwords. Passwords alone are increasingly vulnerable to breaches, whereas MFA adds an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
With cyberthreats constantly evolving and becoming more abundant, MFA provides a crucial defense against various attack vectors, including phishing, brute force attacks and credential theft. According to Alex Weinert, VP Director of Identity Security at Microsoft, a user account is more than 99.9% less likely to be compromised if it leverages MFA.
How does multifactor authentication work?
Now, let’s delve into how MFA operates in practice. Here’s a step-by-step user guide on the technical intricacies of MFA, from enabling it on your account to the verification process during login attempts.
- Enable MFA:
- Start by enabling MFA for your account through the security settings.
- Choose the desired authentication factors, such as SMS codes, authenticator apps or biometric scans.
- Login attempt:
- When you attempt to log in to your account, enter your username and password as usual on the login page.
- Factor request:
- After submitting your credentials, the system prompts you for additional verification.
- Depending on your MFA settings, you’ll be asked to provide one or more factors, such as entering a code sent via SMS or using an authentication app to generate a temporary code.
- Factor verification:
- Enter the required verification code or provide the requested biometric scan.
- The system compares the provided factor against the pre-registered information to validate your identity.
- Access grant/denial:
- If the verification is successful, access to your account is granted and you’re logged in.
- In case of unsuccessful verification, access is denied, and you’ll be prompted to try again or use an alternative method.
What is adaptive multifactor authentication?
In addition to conventional methods, there’s a dynamic approach to MFA known as adaptive multifactor authentication. Adaptive MFA takes security and user experience a step further by intelligently adjusting authentication requirements based on various factors, including the user’s location, device or behavioral patterns. This adaptive approach enhances security without compromising on the user experience, as it can streamline the authentication process when it detects low-risk activities while prompting additional verification in high-risk scenarios.
What authentication factors are commonly used for multifactor authentication?
To fortify digital security, multifactor authentication employs a combination of authentication factors, with each adding a distinct layer of protection. Let’s see in detail the three primary authentication factors integral to MFA systems: knowledge, possession and inherence.
Knowledge factor: Something you know
The knowledge factor refers to information only the user should know, like a password, personal identification number (PIN) or answers to security questions. It’s the most common authentication factor used in multifactor authentication systems, providing a foundational layer of security by requiring users to demonstrate knowledge of a secret piece of information.
Possession factor: Something you have
The possession factor involves something tangible that the user possesses, such as a smartphone, token or smart card. This factor adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to physically possess a device or item to complete the authentication process.
Inherence factor: Something you are
The inherence factor is based on individual physical characteristics or behavioral traits inherent to the user, such as fingerprints, facial recognition or voice patterns. This biometric authentication factor offers a highly secure method of verification, as it relies on individual characteristics that are difficult for unauthorized users to replicate.
What are examples of multifactor authentication?
Multifactor authentication finds widespread application across various domains to enhance security. In this section, let’s delve into some of the real-world use cases to find out how MFA is deployed to fortify authentication processes and safeguard sensitive information.
Remote network access
Organizations often use MFA to ensure secure connections for their employees who are working remotely. After entering the username and password, the users might need to confirm their identity with an authentication token or a temporary code sent to their phone. This step adds an extra layer of security, especially when accessing sensitive company data from outside the organizational network.
Online banking and financial transactions
Financial and banking institutions employ MFA to protect their customer accounts during online transactions. Customers may be asked to provide additional verification, such as answering security questions or entering a code sent to their email or phone, after logging in with their username and password. This helps prevent unauthorized access and fraudulent transactions, giving customers peace of mind while managing their finances online.
Government and military systems
Government agencies and military organizations rely on MFA to safeguard their classified information and secure systems. Personnel accessing these systems typically authenticate using multiple factors, including smart cards, biometric scans and PINs. This stringent security protocol ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data and perform critical operations, protecting national security interests from potential threats.
What are the benefits of multifactor authentication?
In this section, let’s discuss the three key benefits of MFA, shedding light on how it contributes to fortifying security measures, ensuring regulatory adherence and fostering customer trust.
Enhanced access security
Multifactor authentication significantly strengthens access security by necessitating multiple verification methods. Unlike relying solely on passwords, which can be easily compromised, MFA adds layers of protection, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access. This reduces the risk of data breaches, protecting sensitive information and preserving the integrity of business systems.
Regulatory compliance support
Multifactor authentication plays a crucial role in helping businesses meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Many regulatory standards mandate the use of MFA as part of robust security measures to safeguard customer data and prevent unauthorized access. By implementing MFA, businesses demonstrate their commitment to compliance, reducing the likelihood of hefty fines and penalties associated with regulatory violations.
User confidence and trust
Implementing multifactor authentication instills confidence and trust among users, assuring them that their accounts and personal information are well-protected. Knowing that their data is safeguarded with extra layers of security measures, users feel more comfortable engaging with businesses online, whether it’s conducting financial transactions, accessing sensitive information or communicating confidentially. This enhanced trust fosters positive relationships with customers and stakeholders, ultimately contributing to the overall reputation and success of the business.
Why is multifactor authentication a must-have for cloud security
While cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate by offering unprecedented scalability, cost savings and accessibility, it also comes with its fair share of risks. Since cloud services are accessible from anywhere, they are more vulnerable to unauthorized access and data breaches. It is thus important for organizations to completely secure their SaaS data from its growing threat landscape. Multifactor authentication can considerably help on that front by providing an additional layer of security that makes it harder for attackers to gain access to SaaS data.
For more information on best practices for securing SaaS data, check out this whitepaper.
How Spanning helps ensure secure cloud data access
Microsoft has mandated its partner ecosystem to leverage multifactor authentication to keep its SaaS application, Microsoft 365, safe for customers and partners. However, many third-party Microsoft 365 backup solution vendors require their clients to use application-specific service accounts to access Microsoft 365.
While accessing Microsoft 365 via service accounts, the added protection of MFA cannot be utilized since enabling it on a service account may cause the application to break. This creates a very dangerous combination for the organization (the client): service accounts with elevated administrator privileges and no additional protection like MFA. To complicate the scenario further, the third-party application must store this service account’s credentials to be used in day-to-day functions. Even if the credentials are stored securely and encrypted while being used to authenticate, it still expands the client’s attack surface dangerously. Essentially, one breach of your service account could lead to a total data breach.
However, Spanning Backup for Microsoft 365 uses an app-only authorization model called OAuth 2.0, where a Global Administrator grants permissions to the application to access the Microsoft 365 APIs. It can thus function independently of any admin credentials. Spanning implemented OAuth 2.0 as the foundation of our product authentication, not because it is mandatory, but because it adheres to the strictest levels of security for our customers.
Want to learn more about the robust capabilities of Spanning? Get a personalized demo now.